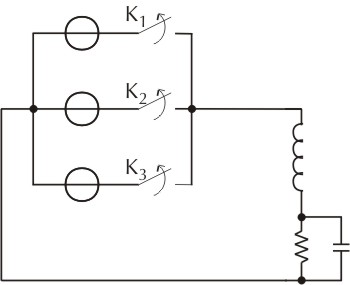
We wish to supply a R-L load with a DC voltage starting from a triphased AC source, Y (star) connected (figure 3).
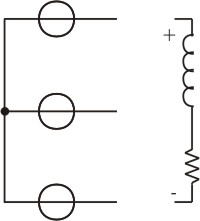
The - terminal of the load is linked to the neutral point of the source.
The + terminal of the load is connected to the three terminals of the source by the way of three semiconductor switches (figure 4).
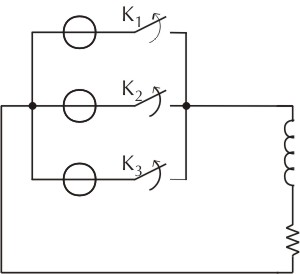
By closing
we obtain a voltage that is approximatively continuous, because it pulsates around its average value (figure 5).
The absorbed current is closer by a constant current when the inductance of the receiver is greater, because this inductance opposes to the current's variations.
If necessary, in order to obtain across the R a quasi constant voltage, a filter can be belt, by adding a capacitor C (figure 6).