The reference directions of the voltage and of the current are the ones from figure 8.
Figure 8: Signs convention as source
With the reference direction chosen for the voltage, a voltage  that is positive means that the potential
that is positive means that the potential 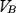 of the B terminal is superior to the potential
of the B terminal is superior to the potential 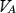 of the A terminal. With the reference direction chosen for the current, a current
of the A terminal. With the reference direction chosen for the current, a current 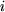 that is positive corresponds to the movement of the positive loads from A to B. The potential of the input terminal being inferior to the one of the output terminal of the current, the dipole provides therefore electrical power. The product
that is positive corresponds to the movement of the positive loads from A to B. The potential of the input terminal being inferior to the one of the output terminal of the current, the dipole provides therefore electrical power. The product ![]() is therefore positive.
is therefore positive.
If  is positive and
is positive and 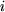 is negative, the potential of the input terminal of the current is superior to the one of the output terminal. The dipole absorbs electrical power. The product
is negative, the potential of the input terminal of the current is superior to the one of the output terminal. The dipole absorbs electrical power. The product ![]() is negative.
is negative.
If  is negative and
is negative and 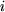 is positive, the load transfer is made from the terminal with higher potential to the terminal with lower potential. The dipole absorbs electrical energy. The product
is positive, the load transfer is made from the terminal with higher potential to the terminal with lower potential. The dipole absorbs electrical energy. The product ![]() is negative.
is negative.
Finally, if both  and
and 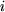 are negative, the load transfer is made from the terminal with lower potential to the terminal with higher potential. The dipole provides electrical power. The product
are negative, the load transfer is made from the terminal with lower potential to the terminal with higher potential. The dipole provides electrical power. The product ![]() is positive.
is positive.
With the sign convention from figure 8, a product ![]() that is positive corresponds to a dipole that provides electrical power. A product
that is positive corresponds to a dipole that provides electrical power. A product ![]() that is negative corresponds to a dipole that absorbs electrical power. It is said to be the signs convention as source. This convention is usually chosen for all the dipoles planned to provide electrical energy (voltage and current sources, the batteries and other electric generators).
that is negative corresponds to a dipole that absorbs electrical power. It is said to be the signs convention as source. This convention is usually chosen for all the dipoles planned to provide electrical energy (voltage and current sources, the batteries and other electric generators).