Enounce of the laboratory
In figure 1 it is presented a schematic view, in section, of a reluctant engine, used for actioning the cutting blades of an electrical razor. With the reel not powered, a resort mentains the relay armature in an eccentric 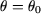 position, fixed to a mechanical limiter (not represented in the figure). If through the reel travels an position, fixed to a mechanical limiter (not represented in the figure). If through the reel travels an 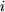 current, an electromagnetic torque will appear which will determine the motion of the relay armature, which will have the tendency to get aligned with the static one. If this current, an electromagnetic torque will appear which will determine the motion of the relay armature, which will have the tendency to get aligned with the static one. If this 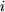 current is an alternative one, with the frequency equal to half of the oscilating frequency of the mechanical system formed from the relay armature and the resort, a sustained oscilatory motion will be obtained. current is an alternative one, with the frequency equal to half of the oscilating frequency of the mechanical system formed from the relay armature and the resort, a sustained oscilatory motion will be obtained.
|
|
|
Each winding of the reel has  whirls. The two windings are connected in series. whirls. The two windings are connected in series.
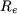 is the medium radius of the air-gap: is the medium radius of the air-gap: 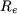 = 28mm = 28mm
-
 is the width of the air-gap: is the width of the air-gap:  = 0,1 mm = 0,1 mm
-
 is the angular opening of the magnetic armatures, at the level of the air-gap: is the angular opening of the magnetic armatures, at the level of the air-gap:  = 9,2° = 9,2°
-
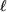 is the width of the engine: is the width of the engine: 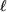 = 28 mm = 28 mm
-
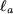 is the thickness of the engine: is the thickness of the engine: 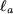 = 12 mm = 12 mm
-
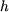 is the medium height of the static armature,at the level of the air-gap : is the medium height of the static armature,at the level of the air-gap : 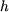 = 37,7 mm = 37,7 mm
-
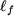 is the medium width of the core of iron: is the medium width of the core of iron: 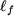 = 7 mm = 7 mm
-
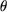 is the angular position of the relay armature compared to the aligning position with fixed armature. is the angular position of the relay armature compared to the aligning position with fixed armature.
|
1. |
The calculus of the torque of electromagnetic origin, assuming the infinite permeability of iron |
|
|
Calculate the electromagnetic torque depending on the 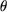 position of the ( position of the (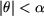 ) rotor and on the ) rotor and on the 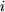 current from the reels. We will consider the section of each reel of 115 mm2 and the medium density of current of j = 1 A/mm2. It will be assumed that the permeability of the iron is infinite and the stray flux negligible. current from the reels. We will consider the section of each reel of 115 mm2 and the medium density of current of j = 1 A/mm2. It will be assumed that the permeability of the iron is infinite and the stray flux negligible.
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Taking into consideration the lenght of the magnetic circuit |
| |
The medium lenght of the magnetic core can be estimated as being (figure 3)
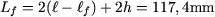
|
| |
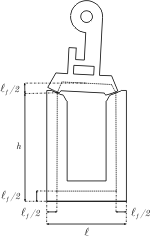
Figure 3: The medium lenght of the magnetic core |
| |
If we consider the relative permeability of iron 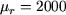 (not infinite), the relation between the lenght of the core and the relative permeability of iron ( (not infinite), the relation between the lenght of the core and the relative permeability of iron (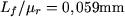 ) is no longer negligible comparing to the relation between the width of the air-gap and the relative permeability of air ( ) is no longer negligible comparing to the relation between the width of the air-gap and the relative permeability of air (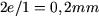 ). To estimate the torque, we must take into consideration the reluctance of the magnetic core. ). To estimate the torque, we must take into consideration the reluctance of the magnetic core. |
| |
|
|
|
|
Resume the calculation of the electromagnetic couple, assuming the relative permeability of iron constant (without saturation) and equal to 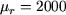 . The stray flux will still be neglected. . The stray flux will still be neglected.
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
3. |
The saturation effect |
| |
|
| |
The ferromagnetic material from which the core is made does not have a constant permeability. The saturation curve is drawn in figure 6.
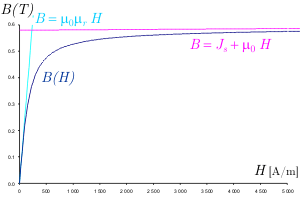
Figure 6: The saturation curve of the ferromagnetic material

|
| |
|
|
|
Assuming that the material is homogeneously saturated through the entire core, calculate for the 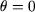 value of the value of the 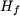 field, deducing the relative permeability of the material in this operating point and calculate the corresponding value of the electromagnetic torque. field, deducing the relative permeability of the material in this operating point and calculate the corresponding value of the electromagnetic torque.
|
| |
|
|